One of the most common questions we get from people is how to utilize supplements to maximize their results. Although science shows that the ketogenic diet is an effective way to lower blood sugar, control insulin resistance, optimize blood lipid levels, and aid in the treatment of some of the most prevalent and lethal conditions, supplements are more alluring than ever before.
In fact, about 145 million Americans use nutritional supplements each year—that’s almost one-half of the population. Unfortunately, most of these supplements are not fulfilling their promises, and the research behind them is shoddy at best.
This is why we decided to dig through the research to find the select few supplements that can truly help you optimize your keto diet. However, before you invest your hard-earned money on the capsules, tablets, and powders that you’ll learn about in this article, let’s put supplementation in the proper perspective.
Should You Add Supplements to Your Keto Diet?
It is hardwired in us to oversimplify complex issues and look for the quick fix.
Have high blood sugar? Just disregard the complicated processes that lead to this condition and take this “blood-sugar lowering supplement.”
Struggling to burn off that extra fat? Just take this natural, plant extract that will shift you into “fat-burning mode.”
The testimonials and “mechanisms” behind how these supplements work all seem so legitimate. This magical powder or pill appears to be precisely what has been missing from your diet plan. The premise is so simple and so seductive that even the most intelligent of us get sucked in.
However, the truth behind what led to your condition and how to reverse it is a lot more complicated. The body is far from simple, and a supplement is seldom the solution to the problem.
Most of the common issues that we struggle with today – such as being overweight, having high cholesterol, and struggling to regulate blood sugar levels – require lifestyle and dietary changes to reverse them for the long-term, which is something that a supplement can’t do.
This is why you MUST make healthy dietary and lifestyle changes and use them (not supplements) as your primary strategy to improve your health and body composition. What you eat and what you do on a daily basis are the two most important variables that determine your results.
Even the most effective supplements will only give you a minor boost in the right direction. If the only thing you change is the supplements you take, then you will always be chasing after a quick-fix that does not exist.
For the most part, the only time you should focus on dietary supplements is after you start forming healthier habits and your health has already begun to improve.
In many cases, diet and lifestyle adjustments are all we need to reach our goals and optimize our health. (This means that you could save that money you were going to waste on supplements and put it toward that vacation you’ve been dreaming about.)
With that being said, if you don’t mind the extra expense, then dietary supplements can be a helpful addition to your healthy lifestyle in many ways – as long as you use the right products for the right reasons in the proper doses.
The Two Primary Strategies for Supplementation
In general, supplements are most effective when used for these two purposes:
- To boost your results in some way
- To avoid nutrient deficiencies
If you are seeking to use supplements simply to meet your micronutrient needs, then it is best to increase your intake of micronutrient-dense foods first. With any dietary change comes an increased risk of nutrient deficiencies.
Keto dieters, in particular, tend to be deficient in one or more of the following vitamins and minerals:
- Biotin
- Iodine
- Potassium
- Magnesium
- Sodium
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin D
To get enough of each one of these nutrients, make sure you are eating a diverse array of meats, poultry, seafood, low-carb dairy, eggs, and veggies. Some of the most micronutrient-dense keto foods are eggs, low-carb vegetables, seafood, and organ meats like beef liver.
For more specific information on how to meet your vitamin and mineral needs while you are on the keto diet, check out our comprehensive guide to micronutrients. In this guide, you will find out how to meet your micronutrient needs with food and how to track your intake.
Once you’ve met your nutrient needs, you are ready to maximize your keto diet results with supplements. To figure out what will help you most, let’s look at scientifically-proven supplements that can help us in a variety of different ways.
What Supplements Should You Take While You Are on the Keto Diet?
Although most supplements aren’t necessary, especially if you are eating plenty of low-carb vegetables and high-quality animal products, you may want to check out the supplements below to help you take your results to the next level.
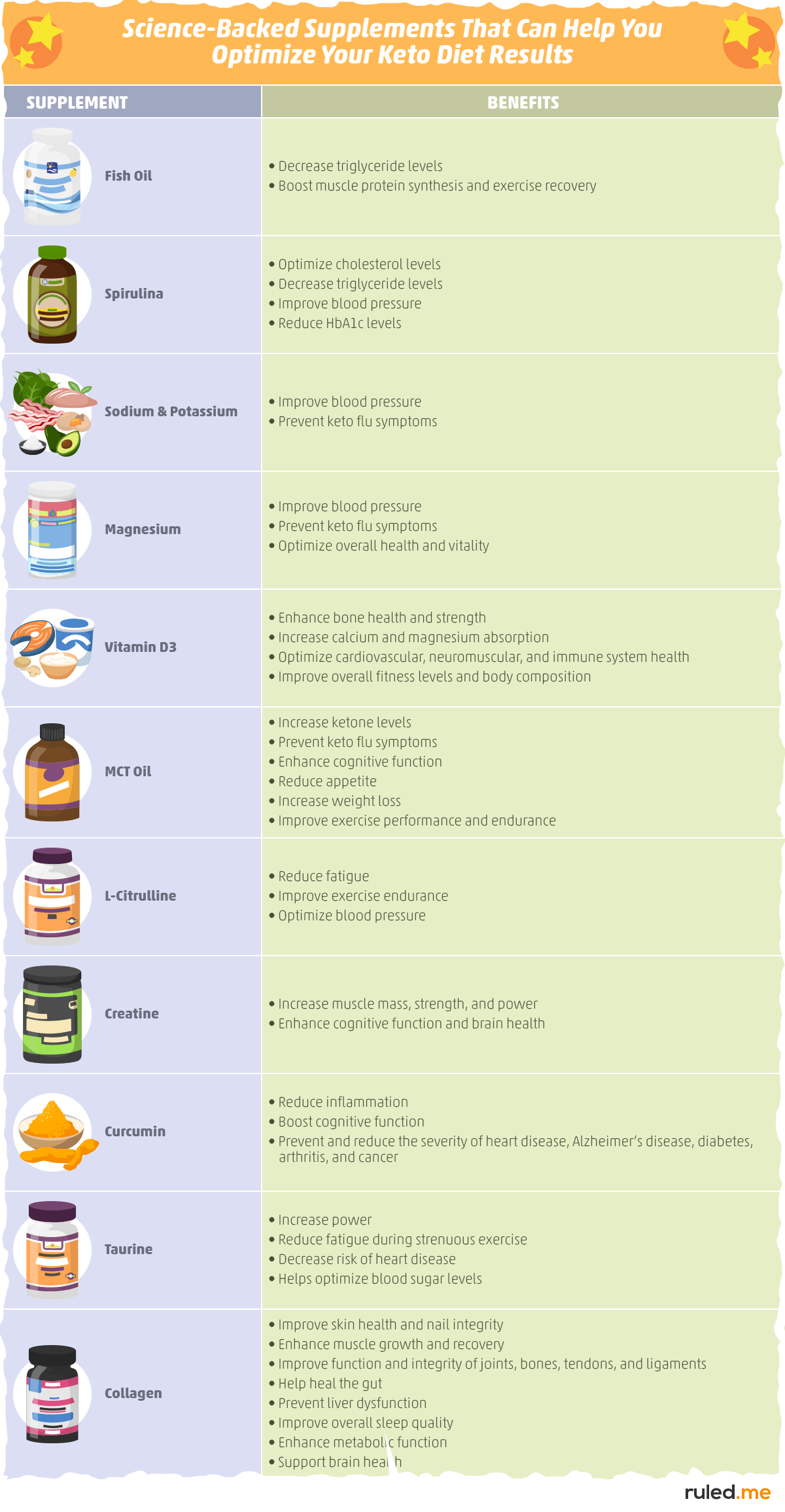
Here’s a list of the science-backed supplements we will learn about in this article:
- Fish oil
- Spirulina
- Sodium and potassium
- Magnesium
- Vitamin D
- MCT oil
- L-citrulline
- Creatine
- Taurine
- Curcumin
- Collagen
- Ketone salts
For a quick guide on these science-backed supplements and how they benefit you, scroll through our graphic below:
For more information on each supplement, the research behind it, and its recommended dosage/use, continue reading. If you noticed that some supplements are missing from the list, we’ll explain why later on in the article.
Fish Oil

According to the Nutrition Business Journal, Americans spend over 1.2 billion dollars on fish oil supplements per year. But what are they exactly and can they benefit your health?
Fish oil supplements are capsules that contain various oils derived from the liver and skin of fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel. They are rich in a special kind molecule called omega-3 fatty acids, a polyunsaturated fat which helps protect against heart disease and potentially a variety of other health conditions related to inflammation.
Omega 3 fatty acids are an essential nutrient. This means that the body doesn’t naturally produce it and you must obtain it through dietary means. (If you’d like to learn more about omega 3 fatty acids and their biological functions, check out our in-depth article on these essential fats.)
The Effects of Fish Oil Supplementation
Recent research suggests that fish oil supplements may lower levels of triglycerides, fat molecules found in the blood that help us store energy for later use. While they are integral to proper body function, elevated levels of triglycerides are linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
In a meta-analysis of 68 studies, scientists examined the impact that daily consumption of 3-4 grams of fish oil had on triglyceride levels in humans. After analysis, researchers observed that regular, daily consumption of fish oil supplements led to an average decrease of 25% in triglycerides in healthy subjects. Subjects with initially higher levels of triglycerides (>200 mg/dl) experienced a more pronounced reduction in triglycerides after supplementation. Interestingly, they also observed that higher supplementation dosages led to greater reductions in triglycerides. As a result of their findings, the authors of the study stated that:
it is clear that practical doses of n-3 fatty acids have a significant and probably clinically important effect on serum triglyceride concentrations, especially in patients with elevated levels of triglycerides.
Even those who have healthy triglyceride levels can benefit from taking fish oil as well. More specifically, the current research indicates that omega 3 supplementation (i.e., taking EPA and DHA) can help improve exercise recovery and stimulate muscle protein synthesis.
This means that fish oil may help you improve your body composition (via boosting muscle growth) while it optimizes your blood lipids.
When this is combined with the keto diet, we end up with a dietary strategy that will help us lose fat, improve health, and look better than ever.
Where to Get Fish Oil Supplements
There are over 50 fish oil supplements available for purchase. However, not all of them should be trusted.
According to trusted supplement adviser Labdoor, almost 50% of fish oil supplements brands don’t contain the daily recommendation of 500 mg of omega-3 fatty acids. Additionally, many of them are contaminated with toxins such as mercury.
So, which fish oil supplement should you take? The highest quality one is manufactured by WHC UnoCardio 1000. The most bang for your buck fish oil supplement in terms of cost and overall quality is the Vitamin Shoppe omega-3 fish oil supplements here. Nordic Naturals Ultimate Omega is a high-quality, trustworthy supplement that we typically recommend as well. The full rankings can be found at the Labdoor website.
Each manufacturer provides recommended daily dosages. However, we suggest consulting with your doctor and dietitian to get a proper assessment of what is best for you.
Key Takeaways: Using fish oil supplements in conjunction with the ketogenic diet can help lower your triglycerides, especially if you already have elevated levels. You can also use fish oil to boost exercise recovery and muscle growth.
Recommendations: If your blood tests indicate that you have elevated levels of triglycerides, a daily dose of at least 3-4 grams of fish oil along with a sound ketogenic diet is an effective method to lower them. You can also get similar (and potentially more) benefits by having 2-3 servings per week of fatty fish.
Spirulina

Spirulina is a common blue-green algae consumed by animals including humans. Interestingly enough, it isn’t a plant; it’s one of the most primitive species on Earth known as a bacterium.
Spirulina comes in two main species: Arthrospria patensis and Arthrospira maxima. Like plants, spirulina is photosynthetic, meaning that it produces its own food in the form of sugar by using the sun’s light.
About 50% of spirulina is composed of complete protein. This means it contains all the amino acids you need. One tablespoon (7 grams) of spirulina contains 4 grams of protein, moderate amounts of fiber, and large quantities of essential nutrients including iron, potassium, and magnesium. It also has been found to improve many critical biomarkers for health significantly.
The Effects of Spirulina Supplementation
The literature on spirulina is much more sparse than that of fish oil, but there is some convincing data supporting the benefits of supplementing with this blue-green algae. In a research study from 2007, for example, 36 healthy subjects (20 women and 16 men) took 4.5 grams of a spirulina supplement per day for six full weeks, and the results were incredible:
- Total cholesterol decreased from an average concentration of 181.7 mg/dL to 163.5 mg/dL, representing a 10.0% decrease.
- LDL cholesterol decreased from an average concentration of 103 mg/dL to 86 mg/dL, representing a 16.5% decrease.
- HDL cholesterol increased from an average concentration of 43.5 mg/dL to an average of 50.0 mg/dL, representing a 12.6% increase.
- Triglycerides decreased from an average concentration of 233.7 mg/dL to 167.7 mg/dL.
- Average systolic blood pressure decreased by 9.2% from 120 mmHg to 109 mmHg.
- Average diastolic blood pressure decreased by 7.0% from 85 mmHg to 79 mmHg.
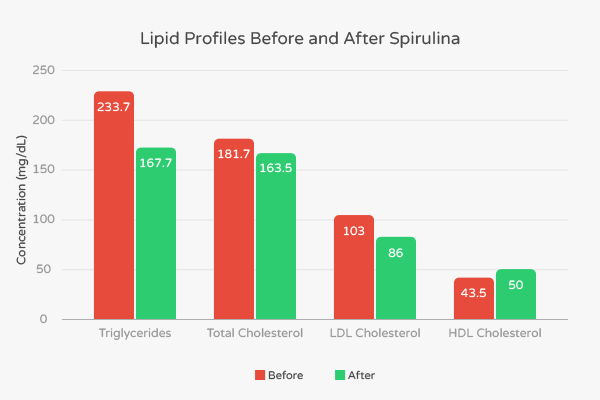
Because of all the positive effects associated with spirulina, the authors stated that:
The present results demonstrate that spirulina maxima has hypolipidemic effects, especially on TC and HDL-C values but indirectly on TC and HDL-C values and positive effects on lowering blood pressure.
Three other high-quality research studies (that we linked in the sources below) found similar effects as well.
Furthermore, spirulina has been found to improve blood sugar levels as well. More specifically, one study found that, when given 2 grams of spirulina for two months, subjects with type 2 diabetes experienced a 1% decrease in HbA1c levels. This is worth noting because studies estimate that a 1% reduction in this marker can lower the risk of diabetes-related death by 21%.
Choosing the Right Brand of Spirulina
If you’re interested in purchase a well-regarded supplement, consider Hawaiian Spirulina Pacifica. Most manufacturers provide a detailed outline on how much spirulina to take and when to take it. You can also buy spirulina in powdered form. Consider throwing it in a cup of water or mixing it into a keto smoothie!
Key Takeaways: Taking spirulina at a moderate dose (4.5 g/day) significantly lowers levels of triglycerides, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, and blood pressure to a reasonable extent while slightly increasing heart-healthy HDL-cholesterol. Additionally, smaller doses (2 grams) of spirulina may help lower HbA1c levels as well.
Recommendation: If your triglyceride levels, total cholesterol, LDL levels, and/or HbA1c levels are elevated to unhealthy levels, consider taking 4.5 g of spirulina per day.
Sodium & Potassium
As we have previously discussed in the piece “Ketogenic Diet and Insulin Resistance,” the ketogenic diet is a highly effective way to reduce insulin levels. This is especially helpful considering that many people in United States and the developed world suffer from type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, or are at risk for developing type 2 diabetes.
Insulin has many functions in the body. It lowers blood sugar by signaling fat cells called “adipocytes” to store this sugar as fat for later energy use. Insulin also tells kidneys to hold on to essential electrolytes such as sodium and potassium and not excrete them.
Because insulin levels go down during a ketogenic diet, your body starts shedding excess sodium and water when you start restricting carbohydrates. While many Americans suffer from high levels of sodium and low levels of potassium, low levels of these two salts in the body is also an issue of concern for people on the ketogenic diet as their body excretes more minerals than usual.
In fact, low potassium and sodium levels are one of the primary reasons why many people on low-carb diets may experience fatigue, lightheadedness, headaches, constipation, and other symptoms of the keto flu that you can read about by clicking this link. Sodium and potassium levels play a crucial role in regulating your blood pressure as well.
The best way to get more sodium and potassium is to consciously add them into your diet. Generally, people on the ketogenic diet should consider adding 2-4 grams of sodium per day. This can be accomplished in a variety of ways. Many keto friendly foods, such as eggs and lean meats, are naturally high in sodium. Sprinkling on some salt or eating some high-fat, salty foods such as bacon or making a low-carb chicken soup might be a good solution.
Potassium is a bit trickier to add in. You can’t start forking over high-carb bananas. However, avocadoes and low-carb vegetables tend to be reliable sources of potassium. A trusted potassium supplement, such as the affordable “Potassium Gluconate” from most stores, might be a good choice as well.
Don’t forget to regularly watch your sodium and blood pressure levels when you increase your sodium intake. Some people may experience unhealthy increases in blood pressure when they add more sodium to their diet. Make sure you consult with your doctor to get checked on these key figures.
Key Takeaways: Because insulin levels are typically lower in people who consume the ketogenic diet, sodium levels might be lower than desired. While adopting the keto diet, potassium intake may be lower than usual as well. This is why it is important to consume the proper amount of sodium and potassium to make sure electrolytes are in healthy levels.
Recommendations: If you are concerned about low sodium levels or you know that your sodium levels are low, consider eating sodium-rich keto-friendly foods such as eggs and lean red meats. Supplement with low-carb vegetable, avocados, and/or potassium gluconate to increase your potassium intake. Be sure to monitor salt and blood pressure to make sure they are in healthy ranges.
Magnesium

Magnesium is an essential mineral that is involved in many critical processes such as moderating blood pressure, synthesizing proteins, maintaining nerve and muscle function, and regulating blood glucose.
Recent literature shows optimal levels of magnesium are important for maintaining adequate levels of testosterone and getting proper amounts of sleep as well.
Magnesium deficiency is relatively common. According to a recent survey study, about 43% of the US population does not meet the USDA dietary intake of magnesium. It tends to be more common among people who consume a low-carbohydrate diet doesn’t have a wide enough variety of plant foods.
If you have low magnesium levels, you may experience fatigue, neurological damage, and muscle cramps, among other things. Oftentimes, however, the symptoms of magnesium deficiency aren’t immediately apparent. Thus, if you want to optimize nutrient status, it is best to consult with a proper blood testing facility to figure out your magnesium levels and see where you are, especially if you are on a low-carb or ketogenic diet.
To ensure adequate magnesium levels and reap the benefits of magnesium, I recommend consuming keto-friendly, magnesium-rich foods regularly. Some examples are avocados, high-fat yogurt, low-carb nuts, and low-carb vegetables. Additionally, it might be helpful to consume high-quality supplements of magnesium. The most trusted brand is “Natural Vitality, Natural Calm.”
Key Takeaways: Magnesium is an essential nutrient in the body with many key functions. Deficiency is common and more prevalent in people who regularly eat a low-carb diet because it increases excretion of ions and many magnesium-rich foods are high-carb.
Recommendations: Most dieticians recommend consuming a daily dosage of 320 mg of magnesium for women and 420 mg of magnesium for men. Consider eating keto-friendly, high magnesium foods such as avocados, low-carb vegetables, and high-fat yogurt. A trusted, high-quality supplement brand might also be helpful. Use blood testing to check your magnesium levels if you’d like to ensure optimal nutrient status.
Vitamin D
Another supplement that is useful to people who follow the ketogenic diet is vitamin D. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble nutrient that also functions as a hormone in the body. It is found naturally in only a few foods, including fatty fish (i.e., tuna, sardines, mackerel) and certain mushrooms. Many dairy products, such as milk and yogurt, are fortified with vitamin D as well.
The body does produce high amounts of vitamin D when exposed to the sun directly (i.e. being outside on a sunny day). Because of this association, vitamin D is often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin.” Prolonged exposure to the sun, however, can increase the risk of skin cancer – so make sure you don’t stay out in the sun unprotected for too long.
Historically, vitamin D is associated with maintaining bone density and strength. However, more recent research has expanded its list of physiological functions. It helps the body absorb minerals such as magnesium and calcium. Furthermore, it helps the body maintain optimal health of the cardiovascular, neuromuscular, and immune system.
Optimal levels of the sunshine vitamin are also crucial for fitness: vitamin D increases muscular power, spurs muscle growth, cuts excess body fat, and may even increase levels of testosterone.
Unfortunately, some of us aren’t reaping the many benefits of Vitamin D. Vitamin D deficiency is very prevalent among the national US population.
In a 2011 estimate conducted by the Centers for Disease Control, about 25% of Americans are at risk for vitamin D inadequacy which is defined as having serum 25(OH)D levels between 30-49 nmol/L. Another 8% were at risk for vitamin D deficiency, defined as having serum 25(OH)D levels less than 30 nmol/L. Thus, about one-third of Americans have low levels of vitamin D.
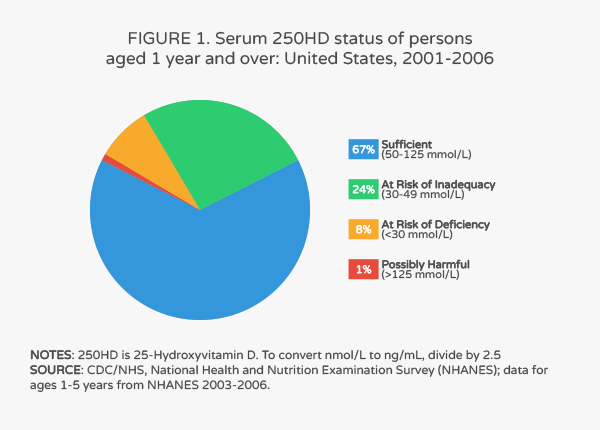
Because vitamin D deficiency is prevalent among the general population and people on a ketogenic diet have a more restricted diet, we strongly recommend that people take 4000 IU/day of vitamin D3.
Another alternative to supplementation is to modify your diet. Thankfully, many vitamin D rich foods, such as fatty fish and fortified dairy, are keto-friendly as well. Additionally, consider spending up to 20 minutes per day in sun to maximize absorption and benefits of vitamin D.
Key Takeaways: Vitamin D is an essential nutrient with many key functions in the body. However, its deficiency is common both in people who do and who don’t consume a ketogenic diet.
Recommendations: If you want to optimize vitamin D levels in your body, consider taking vitamin D3 supplements, soaking up 20 min of sun every day, and eating vitamin D rich foods such as fatty fish.
MCT Oil
Most of the fats that you’ll consume on keto won’t be used as fuel right away, especially during the first few days. This is why supplementing with a special type of fat called MCT oil can help you tremendously.
MCT oil is made of medium chain triglycerides, which are a type of saturated fat that goes straight to the liver after digestion to be used a fuel (just like carbohydrates).
In the liver, they can be converted into ketones and sent to the cells in your body that need them for energy. In other words, supplementing with MCT oil can help you increase your energy levels, adapt to keto, and remedy some of the symptoms of the keto flu.
Research also indicates that MCT supplementation may:
- increase weight loss
- reduce appetite
- improve exercise performance and endurance
- reduce cardiovascular disease risk in some people
- enhance brain health and cognitive function
- improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels
- boost immune system function and regulation
- help regulate gut function
- improve absorption of certain nutrients
- enhance liver cell function
- increase longevity and reduce your mortality risk from heart disease
For a closer look at the research behind these findings, check out our in-depth article on MCTs.
Key Takeaways: MCTs are not essential, but they are one of the most effective supplements for boosting your keto diet results in a variety of ways.
Recommendations: Supplement with 1-2 tablespoons of MCT oil or MCT powder when you need an extra energy boost.
L-Citrulline
L-Citrulline is an amino acid that is commonly used as a sports performance and cardiovascular health supplement.
Studies on exercise performance have found the L-citrulline supplementation results in reduced fatigue and improved endurance for both aerobic and anaerobic prolonged exercise. Other studies indicate that L-citrulline can also help keep blood pressure at healthy levels.
Key takeaways: Citrulline supplements can help reduce exercise fatigue, improve endurance, and optimize blood pressure.
Recommendations: To enhance exercise performance, take 6,000 – 8,000 mg of citrulline malate about an hour before training. To improve blood pressure, take 1,000 mg of citrulline, three times a day with meals, for a total daily dose of 3,000 mg.
Creatine

Creatine is one of the most well-studied supplements and is safe and effective in enhancing many aspects of exercise performance and mental health.
From an exercise perspective, the research indicates that taking 5 grams per day of a cheap monohydrate powder (no need for anything fancy) can help increase muscle mass, strength, and power.
The literature on the impact that creatine supplementation has on mental health, however, is far from conclusive. One double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial found that supplementing with 5 grams of creatine per day had a significant positive effect on both working memory and intelligence. Interventional studies also indicate that higher doses of creatine can be helpful for those who struggle with depression and PTSD.
Key Takeaways: Daily supplementation with creatine can help boost cognitive function, muscular strength, power, and lean mass gains.
Recommendations: Keep it simple and take 5 grams of creatine monohydrate powder per day to experience its benefits.
Curcumin
Curcumin, a bright yellow chemical found in turmeric, has been studied for its potential to prevent and reduce the severity of heart disease, Alzheimer’s, diabetes, arthritis, and cancer. Research also indicates that this potent plant compound can boost cognitive function and reduce inflammation significantly.
One concern about curcumin, however, is that it is poorly absorbed. If you want to ensure that you get all the benefits of curcumin, it is best to purchase one of these four varieties:
- Pairing curcumin with black pepper (piperine)
- Curcumin phytosomes complexed with phosphatidylcholine (Meriva or BCM-95)
- Curcumin nanoparticles (THERACURMIN)
- Water-soluble curcumin (polyvinyl pyrrolidone)
Key Takeaways: Curcumin can help prevent and reduce the severity of many chronic diseases that are linked to inflammation, while also improving overall health.
Recommendations: In general, the current literature indicates that we need to take 80-500mg of a highly-absorbable curcumin supplement daily to experience its benefits.
Taurine
Taurine is an organic acid that is known to have a variety of benefits, especially for bodybuilders and athletes.
In a recent study, researchers compared the effects that caffeine, caffeine + taurine, and taurine had on power and fatigue during an all-out cycling sprint. Astonishingly, taurine supplementation alone decreased fatigue and increased power more than caffeine and taurine together.
Even if you aren’t concerned about exercise performance, taurine may benefit you as well. Here are some examples of the effects that this organic acid may have for you:
- It can reduce the risk of heart disease by improving several key biomarkers, such as cholesterol and blood pressure.
- It has been found to lower blood sugar levels.
- It may improve eye health and help control and calm the nervous system.
Key Takeaways: Not only can taurine help boost exercise performance and decrease fatigue, but it can also help reduce the risk of heart disease and diabetes. It may improve eye and nervous system health as well.
Recommendations: Supplementing with 500-3,000 mg of taurine per day is known to be effective, cheap, and safe.
Collagen
Although collagen is a protein, it does not have the same properties as other more commonly known proteins (e.g., whey, casein, meat, and fish).
In fact, because of collagen’s unique amino acid composition, it provides us with many benefits that extend beyond what we can get from consuming fish, meat, whey, and casein proteins.
For example, here is a brief overview of what collagen supplementation can do for us:
- Improve skin health and nail integrity
- Enhance muscle growth and recovery
- Improve function and integrity of joints, bones, tendons, and ligaments
- Help heal the gut
- Prevent liver dysfunction
- Improve overall sleep quality
- Help with various mental health issues
- Enhance metabolic function
- Support brain health
If you’d like to dig through the research and learn more about this incredible protein, check out our comprehensive article on collagen.
To increase your collagen intake, adding a collagen supplement to your keto smoothies, soups, and sauces or consuming gelatinous bone broth.
If you need help finding high-quality collagen supplements, follow these simple principles:
- Look for collagen hydrolysate, hydrolyzed collagen, or collagen peptides, not gelatin
- Make sure it is sourced from 100% grass-fed cows (or other bovine animals)
- Check the ingredients to make sure that collagen is the only one
- If you want to buy a flavored collagen supplement, make sure it does not contain any added fillers, hidden carbs, or other ingredients that aren’t real foods.
Key Takeaways: Collagen is one protein that we should all be supplementing with because of its unique benefits.
Recommendations: Collagen is effective and safe at virtually any reasonable dose. 10g per day seems to be the minimum dose we need to experience most of its benefits.
Popular Keto Supplements that Aren’t Worth the Money

Ketone Salts
If you are looking to boost your ketone levels, then I wouldn’t recommend investing in ketone salt supplements. Although they do increase blood ketone concentration, it is only short-lived and doesn’t help your body produces its own ketones.
Instead of taking ketone salts, I recommend increasing your MCT intake. MCTs will not only increase your ketone levels, but they will also stimulate ketogenesis (the metabolic process that produces ketones), which is something ketone salts cannot do for you.
With that being said, if you still want to experiment with ketone salts and have the money to invest in them, try to find a supplement that has these three characteristics:
- BHB is the one and only ketone body found in the product.
- It helps you meet your magnesium, potassium, and/or sodium needs (depending on what you are deficient in).
- It also comes with MCTs.
The combination of BHB, MCTs, and essential minerals can make these expensive ketone supplements worth the cost for many keto dieters. However, if you want a cheaper ketone-boosting solution, try restricting carbs and taking MCTs first.
BCAA and EAA Supplements
BCAA stands for branched chain amino acids and EAA is the abbreviation for “essential amino acids.” They both are the building blocks of the complete proteins, like the meat, dairy, and fish, you will have during your ketogenic diet.
After research found that leucine (one of the most prevalent BCAAs) helps stimulate muscle protein synthesis, BCAA supplementation suddenly became “essential” for anyone trying to gain muscle mass.
However, if you are eating plenty of protein already, supplementing with BCAAs or EAAs is just a waste of money. Instead, use that extra money to buy a high-quality protein powder (like whey protein or pea protein) that has all the amino acids necessary for muscle growth.
Carb Blockers
Carb blockers help “block” the breakdown of starches. This renders the starches indigestible, turning a molecule that normally would provide us with 4 calories per gram (and increase our blood sugar levels) into an inert substance that just passes through our digestive tract.
While research has found that carb blockers can help us lose a few extra pounds, it’s not that magic weight loss supplement that many of us hope for.
The gold standard for weight loss is and continues to be a diet that keeps you in a calorie deficit. This has been proven in a plethora of high-quality studies.
If you are looking to lose fat and keep it off, then you would be much better off adopting a low carb diet or keto diet. Cutting the carbs and increasing fat and protein intake is one of the most effective strategies for weight loss.
Putting It All Together — How to Optimize Your Keto Results with Supplements
Although supplements can help boost results and optimize health, they will never be able to replace a healthy diet and lifestyle. Before you even consider taking supplements, it is best to focus your time, money, and energy on implementing a lifestyle and diet plan that works for you.
Ideally, your diet and lifestyle should
- provide you with results that last.
- keep you in a calorie deficit without having to fight against hunger and cravings (if you are trying to lose weight).
- help you maintain healthy biomarkers such as optimal blood sugar, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels.
- improve your gut health, mental health, and overall health.
If your dietary approach has these characteristics, then you probably won’t need supplements at all. However, for those of you who want to boost your results or address nutrient deficiencies, supplementation may be exactly what you need.
For those of you who want to figure out how to meet your vitamin and mineral needs while following the keto diet, check out our guide to micronutrients.
On the other hand, if you are just beginning to change your diet and are not yet ready for supplementation, our guide to starting the keto diet will provide you with the info you need.
Sources
- Plasma Triglyceride Level is a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease Independent of High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level: A Metaanalysis of Population-Based Prospective Studies — Journal of Cardiovascular Risk
- Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. — Circulation
- n-3 fatty acids and serum lipoproteins: human studies. — The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
- Fish oil supplementation alters circulating eicosanoid concentrations in young healthy men. — Metabolism
- Effects of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (ω-3) Supplementation on Some Cardiovascular Risk Factors with a Ketogenic Mediterranean Diet. — Marine drugs
- Nutritional and therapeutic potential of Spirulina — Current pharmaceutical biotechnology
- European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (version 2012). — European Heart Journal
- Serum cholesterol level and mortality findings for men screened in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. — Archives of internal medicine
- Antihyperlipemic and antihypertensive effects of Spirulina maxima in an open sample of Mexican population: a preliminary report. — Lipids in Health and Disease
- The hypolipidaemic effects of Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) supplementation in a Cretan population: a prospective study — Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture
- Effect of Spirulina maxima on postprandial lipemia in young runners: a preliminary report — Journal of Medicinal Food
- Role of Spirulina in the Control of Glycemia and Lipidemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. — NCBI
- Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study – the bmj
- A systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of Spirulina supplementation on plasma lipid concentrations — Clinical Nutrition
- Comparison of isocaloric very low carbohydrate/high saturated fat and high carbohydrate/low saturated fat diets on body composition and cardiovascular risk — Nutrition & Metabolism
- Carbohydrate restriction has a more favorable impact on the metabolic syndrome than a low fat diet — Lipids
- A randomized trial of a low-carbohydrate diet vs orlistat plus a low-fat diet for weight loss — Archives of internal medicine
- Insulin’s impact on renal sodium transport and blood pressure in health, obesity, and diabetes. — American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology
- Potassium and risk of type 2 diabetes — NCBI
- The Interplay between Magnesium and Testosterone in Modulating Physical Function in Men. — International journal of endocrinology
- Magnesium — NIH
- Effectiveness and safety of Vitamin D in relation to bone health – ResearchGate
- The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and Vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: What clinicians need to know — The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease — NCBI
- Systematic review: Vitamin D and calcium supplementation in prevention of cardiovascular events — Annals of Internal Medicine
- Influence of Vitamin D status and Vitamin D3 supplementation on genome wide expression of white blood cells: A randomized double-blind clinical trial — PLoS One
- The influence of winter Vitamin D supplementation on muscle function and injury occurrence in elite ballet dancers: A controlled study. — Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport
- Vitamin D Status, Body Composition, and Fitness Measures in College-Aged Students. — The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research
- Effect of Vitamin D supplementation on testosterone levels in men. — Hormone and Metabolic Research
- Vitamin D supplementation and testosterone concentrations in male human subjects. — Clinical endocrinology
- Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D — NCBI
- Vitamin D status: United States — National Center for Health Statistics
- Recent Developments in Delivery, Bioavailability, Absorption and Metabolism of Curcumin: the Golden Pigment from Golden Spice — NCBI
- Curcumin and Diabetes: A Systematic Review — Hindawi
- Anti-inflammatory Properties of Curcumin, a Major Constituent of Curcuma longa:A Review of Preclinical and Clinical Research — Alternative Medicine Review
- Comparison of systemic availability of curcumin with that of curcumin formulated with phosphatidylcholine — Springer Link
- A Comprehensive Guide to Bodybuilding on the Ketogenic Diet – Ruled.me
- Curcumin — examine
- Oral creatine monohydrate supplementation improves brain performance: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. – NCBI
- Creatine metabolism and psychiatric disorders: Does creatine supplementation have therapeutic value? — NCBI
- Oral L-Citrulline Supplementation Attenuates Blood Pressure Response to Cold Pressor Test in Young Men – American Journal of Hypertension
- What Is Collagen? Everything You Need to Know About This Essential Protein – Ruled.me
- MCT Oil: The Benefits, Risks, and How to Use – Ruled.me
- What Is Taurine? Benefits, Side Effects and More — Healthline
- Branched-Chain Amino Acid Ingestion Stimulates Muscle Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis following Resistance Exercise in Humans – frontiers in Physiology
- Carb Blockers 101: Are They Worth Your Time and Money? – Ruled.me
- Keto OS Side Effects and Benefits: Is It Worth It? – Ruled.me